Today, customers expect delivery at lightning speed. But what if your order started traveling before you even made it? That’s the promise of anticipatory shipping, a predictive logistics model that uses data and AI to pre-position inventory before an order is placed. For modern brands expanding across regions, anticipatory shipping enables faster fulfillment, better planning, and stronger integration across the entire supply chain.
Unlike traditional “order → ship” workflows, anticipatory shipping moves products toward regions or customers based on predicted demand, dramatically reducing delivery times and logistics costs. By doing so, it not only increases operational efficiency but also supports ultra-fast shipping expectations on marketplaces and DTC stores.

What is Anticipatory Shipping?
Anticipatory shipping is a predictive logistics model that pre-moves inventory based on the likelihood of future purchases. Instead of waiting for customer orders, algorithms forecast demand and initiate inventory relocation in advance. The system relies on advanced predictive analytics to move inventory and sometimes even ship products toward geographical areas or potential customers before actual orders are placed.
This approach heavily supports businesses operating across multiple fulfillment centers, giving them the ability to flexibly route goods depending on evolving trends. It also strengthens upstream and downstream warehouse operations as stock moves predictively rather than reactively.
Key differences from traditional fulfillment
| Traditional Shipping | Anticipatory Shipping |
|---|---|
| Order triggers picking & shipping | Predictions trigger inventory movement |
| Delivery speed depends on distance | Delivery speed depends on pre-positioning |
| High reliance on express shipping | Uses inexpensive ground transport early |
| Reactive | Proactive & predictive |
In short, the core difference lies in timing: traditional e-commerce fulfillment waits for a customer to place an order, then initiates a linear fulfillment process of picking, packing, and shipping. The anticipatory shipping model reverses this sequence, relying on forecast accuracy, regional trends, and operational readiness – all areas supported by best practices in ecommerce supply chain management.
Anticipatory Shipping Breakdown
Key components of this revolutionary approach include:
- Predictive analytics engines that process user behavior, browsing activity, purchase history, sales history, and seasonal patterns
- Inventory pre-positioning in regional hubs or multiple fulfillment centers based on forecasted demand, supporting buffer inventory strategies during peak seasons.
- Late-select addressing technology that allows a shipped package to begin transit with incomplete destination information
- Real-time data integration from IoT sensors, RFID tracking, data sources, and warehouse management systems
The ultimate goal extends beyond faster delivery times; it’s about creating an enormous competitive advantage through operational efficiency. By shipping products using standard ground transportation to regional hubs before orders occur, companies can offer expedited shipping experiences while avoiding the substantial additional cost of premium shipping services.
This approach transforms customer expectations by making ultra-fast delivery the norm rather than the exception. When inventory is pre positioned near customers, even standard shipping methods can deliver merchandise immediately within the same day or next day timeframe.
Tip: When explaining anticipatory shipping to non-technical stakeholders, frame it as “Amazon-style delivery for your own brand” powered by data-driven predictions instead of guesswork.
The Technology Behind Amazon Anticipatory Shipping
At the heart of anticipatory shipping are sophisticated machine learning models that continuously analyze user behavior patterns across multiple data sources. Modern anticipatory shipping platforms integrate artificial intelligence with machine learning algorithms to achieve prediction accuracy rates between 85–90% for high-velocity product categories.
Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning Models
At the heart of anticipatory shipping are sophisticated machine learning models that continuously analyze customer behavior patterns and sales history data across multiple sources. These same data structures underpin modern ai stock management tools, making inventory forecasting more precise.
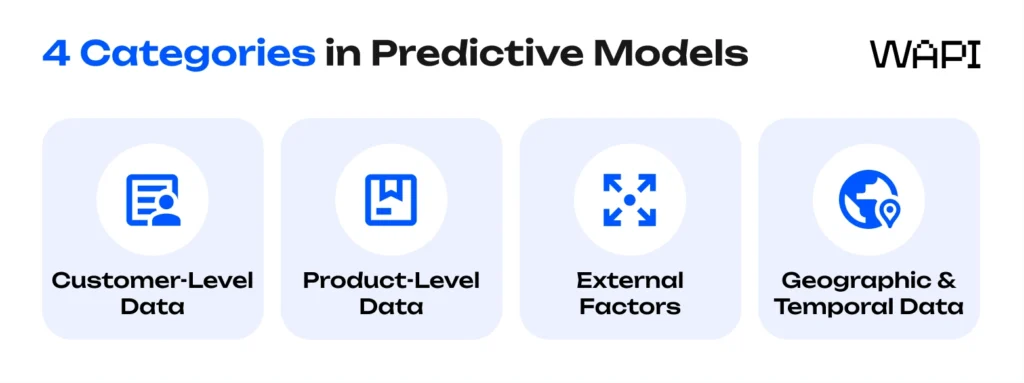
The models typically work with four key data categories:
- Customer-level data: Includes browsing history, previous purchases, carts, wishlists, search queries, and device usage patterns. Advanced systems track metrics like page dwell time and click-through paths to build granular customer profiles.
- Product-level analytics: Monitors SKU performance, lifecycle stages, seasonality, and cross-selling patterns. Here, the term stock keeping unit becomes critical because anticipatory shipping depends on granular product-level forecasting. The system learns which products are frequently bought together and can predict likely complementary purchases.
- External factors: Weather, local events, economic indicators, and regional preferences can dramatically shift demand. For instance, algorithms might increase the likelihood of umbrella sales in Seattle during rainy weeks or boost electronics forecasts in university towns during back-to-school periods.
- Geographic and temporal data: Helps identify regional demand clusters and the optimal timing for inventory movements. The system continuously recalibrates as demand shifts between regions and time windows.
These neural networks ingest real-time signals, such as viral product spikes or sudden weather changes, and adjust forecasts dynamically. When patterns change, a pre-positioned shipped package may be rerouted automatically to match the new demand.
Pre-positioning and Inventory Management
Predictive models determine where inventory should sit before customers click “buy.” How?
- Algorithms identify high-probability demand zones
- Inventory is moved into regional hubs or micro-fulfillment centers
- Systems continuously rebalance stock as trends shift
- Automated robotics (e.g. Kiva robots) streamline pre-packing and routing
Partial geographic identifiers (like the first three digits of a postal code) guide shipped package routing before full addresses are known, supporting efficiency across the broader logistics network. This aligns perfectly with the foundation of stock control, ensuring businesses avoid overstock or shortage scenarios.
Amazon’s Anticipatory Shipping Patent and Implementation

Amazon’s groundbreaking approach to predictive shipping began with their December 2013 Amazon’s anticipatory shipping patent filing. This patent laid the foundation for what would become one of the most significant innovations in modern logistics, especially platforms offering fulfilled by TikTok or cross-border commerce where predictive positioning ensures faster delivery despite geographical distance.
The patent describes how Amazon predicts demand, pre-packs items, and injects them into the common carrier network before a customer finalizes an order. The system can move these packages into carrier networks or position them at regional facilities, dramatically reducing the time between order placement and delivery.
What makes this approach particularly innovative is its use of partial addressing. Packages can enter the shipping network with incomplete destination information – perhaps only the first few digits of a postal code – allowing them to travel through most of their route while final address details remain undetermined. By pushing a shipped package into transit early, Amazon can deliver within hours of the customer’s order date; a radical shift in expectations.
Late-Select Addressing Technology
Late-select addressing allows a shipped package to travel most of its route without a complete address. It’s a powerful concept also used for managing waybill routing types, enabling dynamic carrier-level adjustments and preventing delays during customs or hub transfers.
How Late-Select Addressing Works: Overview
- A predictive algorithm identifies a product with a high probability of being ordered in a specific region within 24–48 hours.
- The system triggers pre-packing of that item and assigns it a partial address (e.g., the three most significant digits of likely postal codes).
- The shipped package enters the carrier network and travels through sorting facilities toward the target region, tagged with barcodes or RFID for real-time visibility.
- When a customer order matches that pre-positioned inventory, the system electronically assigns the full address and updates carrier systems.
- The package is routed to its final destination, often arriving the same day the order is placed.
If no matching order appears within the predicted window, the shipped package may be redirected to another high-probability region, returned to a fulfillment center, or repurposed for local marketing efforts (for example, flash sales or same-day offers).
Amazon’s implementation evolved from this patent concept into their Prime delivery network, which now serves over 200 million subscribers globally through more than 1,000 fulfillment facilities worldwide. The company’s ability to offer same-day and next-day delivery on millions of items stems directly from these anticipatory logistics principles.

Key Benefits of Amazon Anticipatory Shipping
The advantages of anticipatory shipping go far beyond basic speed improvements. Done well, it creates a compound advantage across cost savings, customer experience, and strategic positioning.
1. Dramatically Faster Delivery
Traditional models often require 3–5 business days for standard delivery. Anticipatory shipping can reduce this to same-day or next-day for a large share of orders by placing inventory closer to demand.
2. Financial and Operational Benefits
Companies reduce transportation costs, avoid overstock mistakes, and increase turnover. This improves overall fulfillment network performance.
- 15–30% savings compared to heavy reliance on expedited shipping
- Last-mile optimization, which is critical given that last-mile often represents ~50% of total shipping cost
- Higher inventory turnover, thanks to more accurate demand prediction
- Fewer stockouts and fewer “dead” SKUs sitting in the wrong warehouse
3. Stronger Customer Metrics
Faster, more reliable delivery tends to improve:
- Customer satisfaction and NPS
- Repeat purchase rates and lifetime value
- Review scores and word-of-mouth referrals
4. Better Data for the Whole Business
The same data used to power anticipatory shipping can feed:
- Personalized marketing campaigns
- Smarter pricing and discounting strategies
- More informed product development decisions
Tip: Use logistics data in your marketing stack – tie “delivered in X hours” performance to campaign messaging to prove your promise in real numbers.
Challenges and Implementation Risks
Despite its potential, anticipatory shipping is not “plug and play.” It requires investment, change management, and careful risk control.
1. Capital and Infrastructure
Full-scale implementation for large retailers may require multi-billion-dollar investment in:
- Fulfillment network expansion
- IT and data infrastructure
- Advanced analytics and AI platforms
- Carrier and last-mile partnerships
2. Prediction Accuracy and Over-Shipment
Even a small error rate can be expensive.
If models overestimate demand in a region, companies risk:
- Surplus inventory that must be discounted or moved. Misforecasting creates overstock in the wrong regions – one substantial disadvantage of a predictive system.
- Higher internal transport costs for rebalancing
- Missed opportunities in regions where stock is insufficient
3. Integration Complexity
Most organizations still rely on legacy WMS, OMS, and ERP systems not originally built for anticipatory flows. Integrating:
- Real-time data
- AI prediction engines
- Multi-node fulfillment orchestration
often requires significant custom development and phased rollouts.
4. Data Privacy and Regulation
The heavy reliance on customer data raises serious questions around GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy frameworks. Companies must:
- Create transparent data usage policies
- Offer meaningful consent/opt-out mechanisms
- Ensure cross-border shipping and taxation rules are respected, especially when shipping with partial addressing.
Implementation Strategies for Different Business Sizes
Before you jump into anticipatory shipping, it helps to understand how your business size influences the way you should approach it. Not every company needs (or can sustain) an Amazon-level operation, but almost every business can apply anticipatory principles in a way that improves efficiency and delivery speed.
Large Retailers & Marketplaces
Large retailers with significant resources can pursue a full-scale anticipatory shipping model. This typically means investing in advanced predictive analytics platforms and in-house data science teams, expanding logistics networks with regional hubs and micro-fulfillment locations, and integrating late-select addressing directly with carrier systems to enable pre-shipment with partial addresses. For companies at this scale, anticipatory shipping becomes a long-term strategic capability that delivers substantial competitive advantages and operational efficiencies, often enough to justify the high upfront investment.
Mid-Size E-commerce Businesses
Mid-size companies usually benefit most from a more targeted approach. Instead of transforming their entire logistics model, these businesses focus anticipatory shipping on best-selling products and the regions with the highest sales volume. They often use pre-positioning during peak seasons – such as Black Friday, holidays, or major campaigns – when delivery speed has the greatest impact on conversion rates. Prediction models are typically layered on top of the existing WMS and analytics tools rather than building a new tech stack from scratch. Success here comes from measurable progress: shorter delivery times, reduced spending on express shipping, and improved repeat purchase rates.
Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Smaller brands can still apply anticipatory shipping principles without building new warehouses or complex systems. Many rely on 3PLs or fulfillment networks that already offer multi-location inventory distribution and basic forecasting. SMEs can use their own historical sales data to pre-position only a handful of products in one or two key regions, making demand forecasting manageable and cost-effective. Tools like Google Analytics, Klaviyo, and simple BI dashboards help identify where orders cluster geographically or which products sell repeatedly in certain areas. Some SMEs also collaborate with regional carriers or local couriers to strengthen last-mile delivery. The most effective approach is to begin with a small pilot – one SKU, one region, or one season – and gradually scale once the model proves its value.
Real-World Applications of Amazon Anticipatory Shipping
The practical implementation of anticipatory shipping extends far beyond Amazon’s pioneering efforts, with various retailers and logistics companies adapting the core principles to their specific operational contexts and customer bases.
Amazon’s success with Prime delivery in major metropolitan areas like New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago demonstrates the scalability of anticipatory logistics. The company’s ability to offer same-day delivery on millions of products stems from sophisticated demand prediction algorithms combined with dense networks positioned throughout urban centers.
Walmart has responded with its own interpretation of anticipatory logistics through local fulfillment centers and integration with curbside pickup services. While not implementing full anticipatory shipping, Walmart uses predictive tools to optimize inventory placement across stores, enabling rapid order fulfillment for online purchases through store pickup and local delivery.
Target’s ship-from-store model represents an alternative approach to anticipatory shipping principles. By using retail locations as mini-fulfillment centers, Target can position inventory close to customers based on local demand patterns. When online orders are placed, the system identifies the optimal store location for fulfillment, often enabling same-day delivery within local markets.
These implementations reveal common patterns: successful anticipatory shipping requires deep integration between predictive analytics, physical infrastructure, and operational processes. The most effective systems combine technological sophistication with practical understanding of local market conditions and customer behaviors.
The Future of Anticipatory Shipping
Anticipatory shipping will accelerate rapidly as key technologies mature, enabling faster decision-making, smarter forecasting, and more efficient delivery networks. The developments below represent the most meaningful shifts shaping the future of predictive logistics.
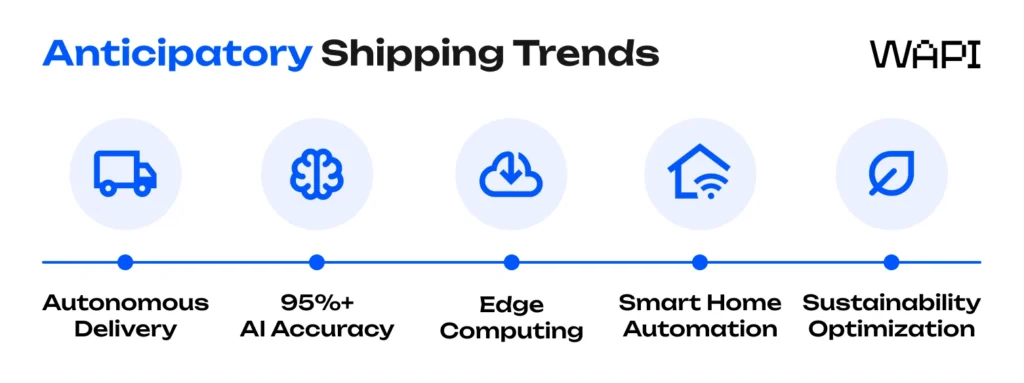
- Autonomous delivery and drones will transform last-mile logistics by removing labor constraints and enabling continuous, on-demand transport. Predictive systems may soon pre-position inventory inside autonomous vehicles already circulating in high-probability areas, allowing orders to be fulfilled almost instantly once placed.
- Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) will expand across urban areas, bringing automated and highly efficient storage closer to customers. These compact facilities shorten last-mile distances, support hyper-local forecasting, and make anticipatory shipping viable even in densely populated cities. Their growth over the next several years will dramatically increase delivery speed and consistency.
- AI models achieving 95%+ accuracy will reduce misplacement risks and unlock anticipatory shipping for a broader range of products. As data quality improves and models become more sophisticated, retailers will confidently pre-position mid-velocity and even niche items with far lower financial risk.
- 5G networks will enable real-time responsiveness, with ultra-low latency allowing systems to adjust routes, update order priorities, and rebalance inventory within seconds. This infrastructure makes anticipatory networks far more agile during sudden demand spikes, weather changes, or viral product trends.
- Edge computing in fulfillment centers will supercharge automation by enabling robots and warehouse systems to process information locally rather than relying on centralized servers. This makes picking, packing, and routing decisions nearly instantaneous, improving both speed and accuracy in anticipatory operations.
- Smart home and IoT integrations will provide highly reliable consumption data that triggers predictive replenishment before customers run out of everyday products. This brings anticipatory shipping closer to “invisible logistics,” where restocking happens automatically based on real usage patterns rather than manual ordering.
- Sustainability requirements will push anticipatory systems to optimize not only for speed and cost but also carbon efficiency. Companies will shift toward more regionalized inventory placement, cleaner last-mile options, and predictive models that reduce unnecessary transportation. Environmental performance will increasingly be part of every logistics decision.
Together, these developments indicate that anticipatory shipping will evolve from an advanced capability used by large tech companies into a mainstream logistics strategy. As predictive systems become more accurate, affordable, and automated, businesses across all sectors will shift from reactive fulfillment to proactive, data-driven delivery models.
Conclusion
Anticipatory shipping marks a shift from reactive logistics to predictive commerce. By combining AI, data, and tools like optimized first mile delivery, it becomes a transformative asset for e-commerce brands.
Organizations considering anticipatory shipping should start by assessing their data maturity, infrastructure readiness, and product mix, then launch focused pilots rather than attempting a full-scale transformation at once. Even partial adoption of predictive logistics principles can unlock meaningful gains, and lay the groundwork for more advanced implementations in the future.



 Community
Community
